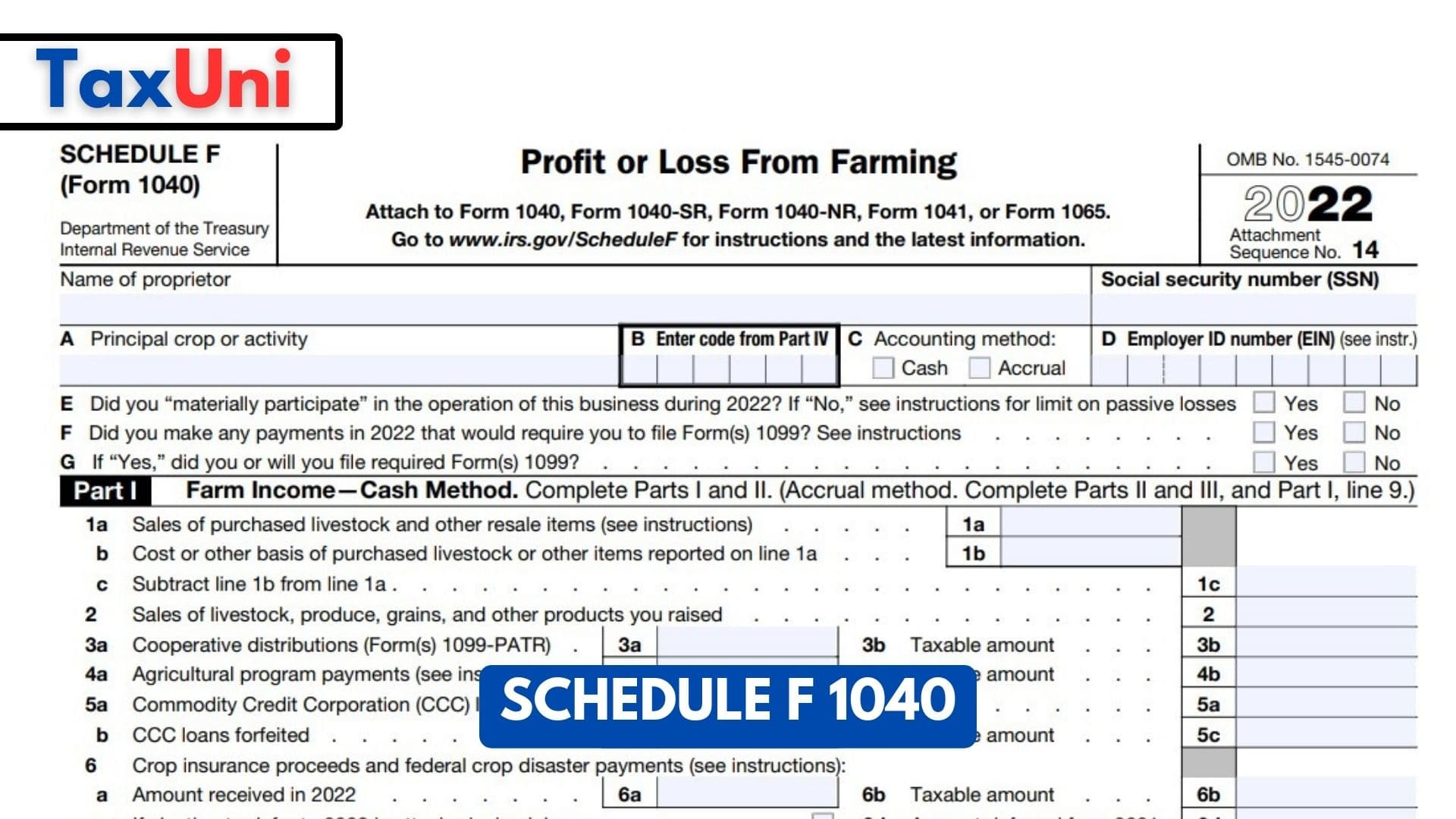
Farming is a unique profession that requires individuals to report their income and expenses to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Schedule F – Profit or Loss from Farming is a form that allows farmers to report their income, expenses, and other details related to their farming operations. It is a crucial part of the annual tax return for farmers who must file a Schedule F to report their farming income. If you earn a profit or incur a loss from your farming activities, you must file Schedule F. This applies to farmers who operate their farms as sole proprietors or as members of a partnership. It also applies to farmers with rental income from farming activities or receiving payments under a crop-sharing arrangement.
Farming activities include the cultivation of crops, raising livestock or poultry, and producing dairy products or other commodities. It also includes activities related to the production of fruits, vegetables, and nuts. It is essential to note that even if you do not profit from your farming activities, you must still report your income and expenses on Schedule F if your gross income from farming is $400 or more. This is because the IRS considers farming activities a business, and all businesses must report their income and expenses, regardless of whether they profit.
Farmers must file Schedule F along with their tax return using Form 1040. If you operate your farm as a sole proprietor, you must report your farming income and expenses on Schedule F and attach it to your Form 1040. If you operate your farm as a partnership, you must report your share of the farming income and expenses on Schedule K-1 (Form 1065), which is then reported on your tax return.
What is the Cash Method?
The cash method is the simpler of the two methods and is often used by small businesses and farmers. Under the cash method, income is recorded when it is received, and expenses are recorded when they are paid. For example, if you sell a crop in December but do not receive payment until January, you would record that income on your tax return for the year in which you received the payment (i.e., January of the following year). Similarly, if you purchase seed in December but do not pay for it until January, you would record that expense on your tax return for the year in which you paid for it (i.e., January of the following year).
What is Accrual Method?
On the other hand, the accrual method records income and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when payment is received or made. For example, if you sell a crop in December but do not receive payment until January, you would still record that income on your tax return for the year in which you sold the crop (i.e., December of the current year). Similarly, if you purchase seed in December but do not pay for it until January, you would still record that expense on your tax return for the year in which you purchased the seed (i.e., December of the current year).
How to Fill Out Schedule F?
Part I – Farm Income – Cash Method
- Line 1a: Livestock item sales
- Line 1b: Costs of items reported on 1a.
- Line 1c: Subtract line 1b from line 1a
- Line 2: Sales of livestock, produce grains, and other products.
- Line 3a: Cooperative distributions (Form(s) 1099-PATR)
- Line 4a: Agricultural program payments.
- Line 5a: Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) loans.
- Line 5b: CCC loans forfeited
- Line 6: Crop insurance proceeds and federal crop disaster payments.
- Line 6a: Amount received in 2022.
- Line 6c: If election to defer to 2023 is attached, check here.
- Line 7: Custom hire income
- Line 8: Other Incomes (federal and state gasoline or fuel tax credit or refund include
- Line 9: Gross income (Add lines 1c, 2, 3b, 4b, 5a, 5c, 6b, 6d, 7, and 8) enter the amount from Part III, line 50.
Part II Farm Expenses—Cash & Accrual Method
- Line 10: Car and truck expenses. Attach Form 4562.
- Line 11: Chemicals.
- Line 12: Conservation expenses.
- Line 13: Custom hire (machine work).
- Line 14: Depreciation and Section 179 expenses.
- Line 15: Employee benefit programs. (other than on line 23).
- Line 16: Feed
- Line 17: Fertilizers and lime
- Line 18: Freight and trucking
- Line 19: Gasoline, fuel, and oil
- Line 20: Insurance (except health)
- Line 21: Interest
- Line 21a: Mortgage
- Line 21b: Other
- Line 22: Labor hired
- Line 23: Pension and profit-sharing plans
- Line 24: Rent or lease
- Line a: Vehicles, machinery, equipment
- Line b: Other (land, animals, etc.)
- Line 25: Repairs and maintenance
- Line 26: Seeds and plants
- Line 27: Storage and warehousing
- Line 28: Supplies
- Line 29: Taxes
- Line 30: Utilities
- Line 31: Veterinary, breeding, and medicine
- Line 32: Enter other expenses (specify)
- Line 32a:
- Line 32b:
- Line 32c:
- Line 32d:
- Line 32e:
- Line 32f:
- Line 33: Total expenses. Add lines 10 through 32f. If line 32f is negative.
- Line 34: Net farm profit or (loss). Subtract line 33 from line 9.
- Line 35: reserved line.
- Line 36: Check the box appropriate for your investment status. (It is at risk, or some of it is not at risk).
Part III Farm Income: Accrual Method
- Line 37: Sales of livestock, produce, grains, and others.
- Line 38: Cooperative distributions (Form(s) 1099-PATR)
- Line 39: Agricultural program payments
- Line 40: Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) loans
- Line 40a: CCC loans reported under election
- Line 40b: CCC loans forfeited
- Line 41: Crop insurance proceeds
- Line 42: Custom hire (machine work) income
- Line 43: Other Income
- Line 44: Add amounts in lines 37, 38b, 39b, 40a, 40c, 41, 42, and 43
- Line 45: Inventory of livestock, produce, and grains at the beginning of the year. (Form 4797 sales not included).
- Line 46: Cost of livestock, produce, grains, and other products purchased during the year
- Line 47: Add lines 45-46
- Line 48: Inventory of livestock, produce, grains, and other products at the end of year.
- Line 49: Subtract line 48 from line 47. Cost of livestock, produce grains, and other products sold.
- Line 50: Subtract line 49 from line 44. Enter the result here and on Part I, line 9
Principal Agricultural Activity IRS Business Codes
Crop Production
111100 Oilseed and grain farming
111210 Vegetable and melon farming
111300 Fruit and tree nut farming
111400 Greenhouse, nursery, and floriculture production
111900 Other crop farming
Animal Production
112111 Beef cattle ranching and farming
112112 Cattle feedlots
112120 Dairy cattle and milk production
112210 Hog and pig farming
112300 Poultry and egg production
112400 Sheep and goat farming
112510 Aquaculture
112900 Other animal production
Forestry and Logging
113000 Forestry and logging (including forest nurseries and timber tracts)
113110 Timber tract operations
113210 Forest nurseries and gathering of forest products
113310 Logging